Collaborative Intelligence Systems Lab
Cooperative Multi-Modal Perception
Autonomous Vehicle Drive-by-Wire Systems
SEE-V2X: C-V2X Communication Dataset
Driving via Keyboard
Research Highlights
- Cooperative Autonomy: AVR [Mobisys'18], CarMap [NSDI'20], Coopernaut [CVPR'22], AutoCast [Mobisys'22], ELM [ECCV'24], Harbor [Sensys'24], CMP [RA-L'25], CATS [TVT'25], SEE-V2X [Sensys'25]
- System for Edge ML: FedML [NeurIPS'20(SpicyFL)], ML-EXray [MLSys'22], MCAL [ICLR'23], WOMD-LIDAR [ICRA'24]
- Video Delivery & Analytics: CoBCast [Mobihoc'16], Kestrel [IoTDI'18]
- Vehicular Sensing: CarLog [Sensys'14], CarLoc [Sensys'15], ContextSensing [TVT'17]
Select Media Coverage
The Reference Desk, Oct 17, 2025
National Science Foundation, August 25, 2025
Waypoint, The Official Waymo Blog, March 16, 2023
Embedded Computing Design, March 03, 2022
New episode of The Reference Desk podcast drops this Friday, October 17! Dr. Hang Qiu discusses autonomous systems, mobile sensing, wireless networking, and how they are shaping the future of connected and automated vehicles and intelligent transportations.
National Science Foundation, August 25, 2025
Awardees will demonstrate technological solutions that transform the nation's economy and benefit all Americans, from enabling autonomous vehicles to making remote medical procedures possible.
Waypoint, The Official Waymo Blog, March 16, 2023
WOMD-LIDAR augments Waymo Open Dataset with high-resolution LiDAR data. This enhancement enables end-to-end motion prediction in Waymo 2023 Challenges.
Embedded Computing Design, March 03, 2022
The increasing deployment of embedded AI and ML at the edge has certainly introduced new performance variations from cloud to edge. Despite the abrupt negative change in AI execution performance on the edge device, the adoption of TinyML is a way to move forward.
Cooperative Autonomy
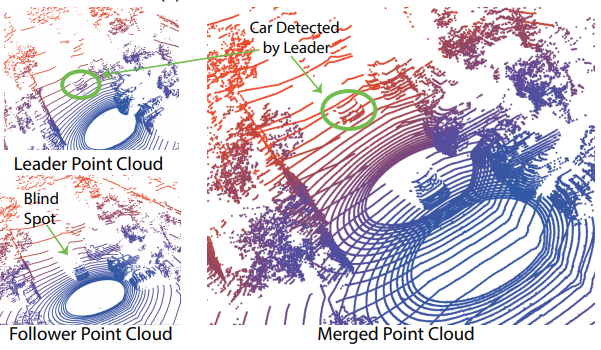
- Cooperative Perception. Autonomous vehicles use 3D sensors (e.g. LiDAR, camera, RADAR) to sense the environment. However, these 3D sensors only provide line-of-sight (LoS) perception and obstacles can often occlude their field-of-view (FoV). Cooperative perception enables sensor sharing in real time, leveraging additional vantage points to build extended view beyond occlusion and sensing range. Collaborating with General Motors, our award-winning work Augmented Vehicular Reality (AVR) first demonstrates the feasibility with an end-to-end prototype. AutoCast then solves the network bottleneck to enable cooperative perception at scale, delivering augmented view to every vehicle on demand.
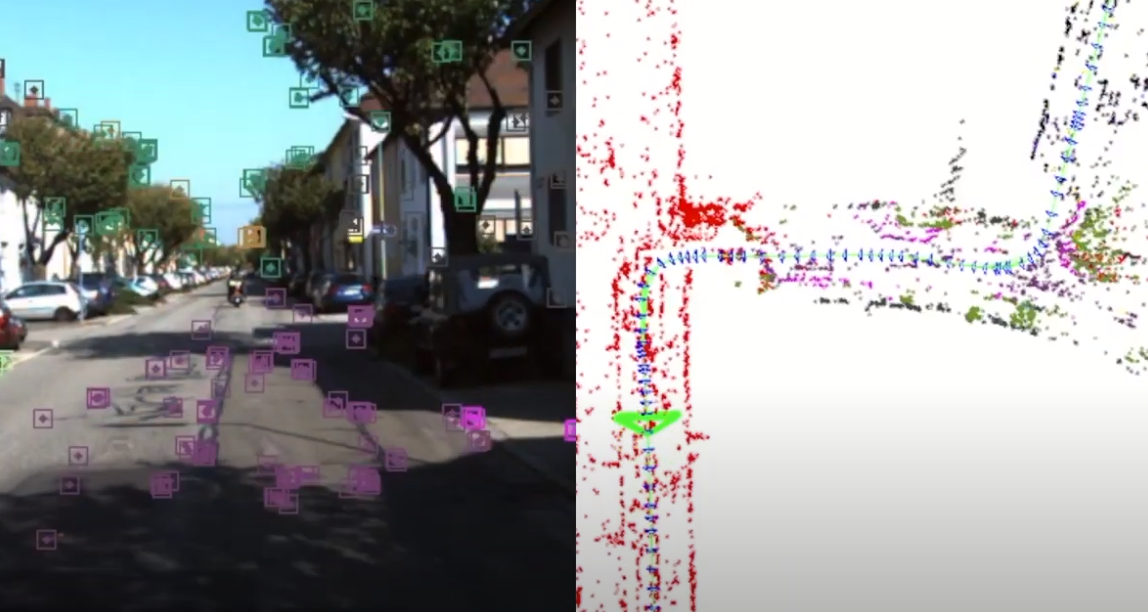

- Self-healing Map, Map-less Robots. High-definition Map (HDMap) has been a crucial component for fine-grained localization. Collecting this map can be tedious and expensive. What exacerbates the problem is its vulnerability to changes (e.g. construction, road closures) in safety-critical applications. Self-healing map aims to detect those changes and update the map in near-real time. Map-less robots targets onboard mapping and navigation without any prior knowledge of the world. Partnering with General Motors, our work CarMap takes a crowdsourcing approach, and creates a lightweight map change representation for fast broadcasting, while being feature-rich for robust localization.
- Cooperative Driving, End-to-end Driving. With cooperative perception, the next question is how to effectively leverage shared information to make better driving decisions. What data is most critical to influence decisions, what kind of representation for that data should be used, how to design the interface to accept that representation. Our Coopernaut takes a holistic approach, enabling end-to-end training with shared sparse point features, which can be broadcasted to all nearby vehicles and swiftly transformed into different perspectives.
Edge ML System
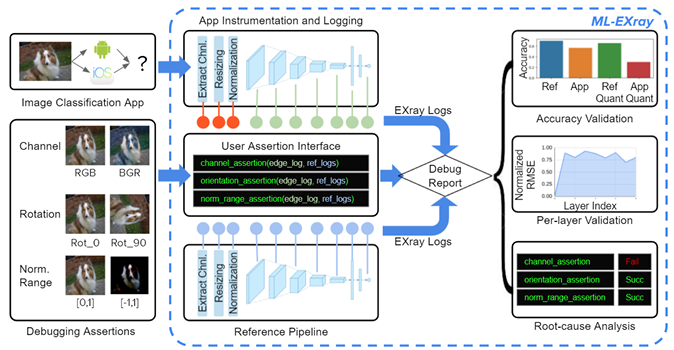
- Edge MLOps, Deployment, Monitoring, Update. Robot intelligence powered by Edge ML is the core component of collaborative intelligence. Recent years have seen a shift of these models from serving on the cloud to being deployed on the actual edge devices, to enable low-latency, low-power, privacy-sensitive applications (e.g. autonomous cars, personal assistants, ads recommendation). More often than not, however, the real-world performance can be below expectation, and there lacks the proper tooling to understand why. One key solution is to apply Machine Learning Operations (MLOps) to edge robots, developing a series of peripheral systems around deployment, monitoring, and model retrain and update. Collaborating with Google and New Relic, our award-winning work ML-Exray offers such a framework, provides visibility into layer-level details of edge ML execution, enabling debugging, monitoring, and potential automated loop of retrain and deployment (CI/CD).
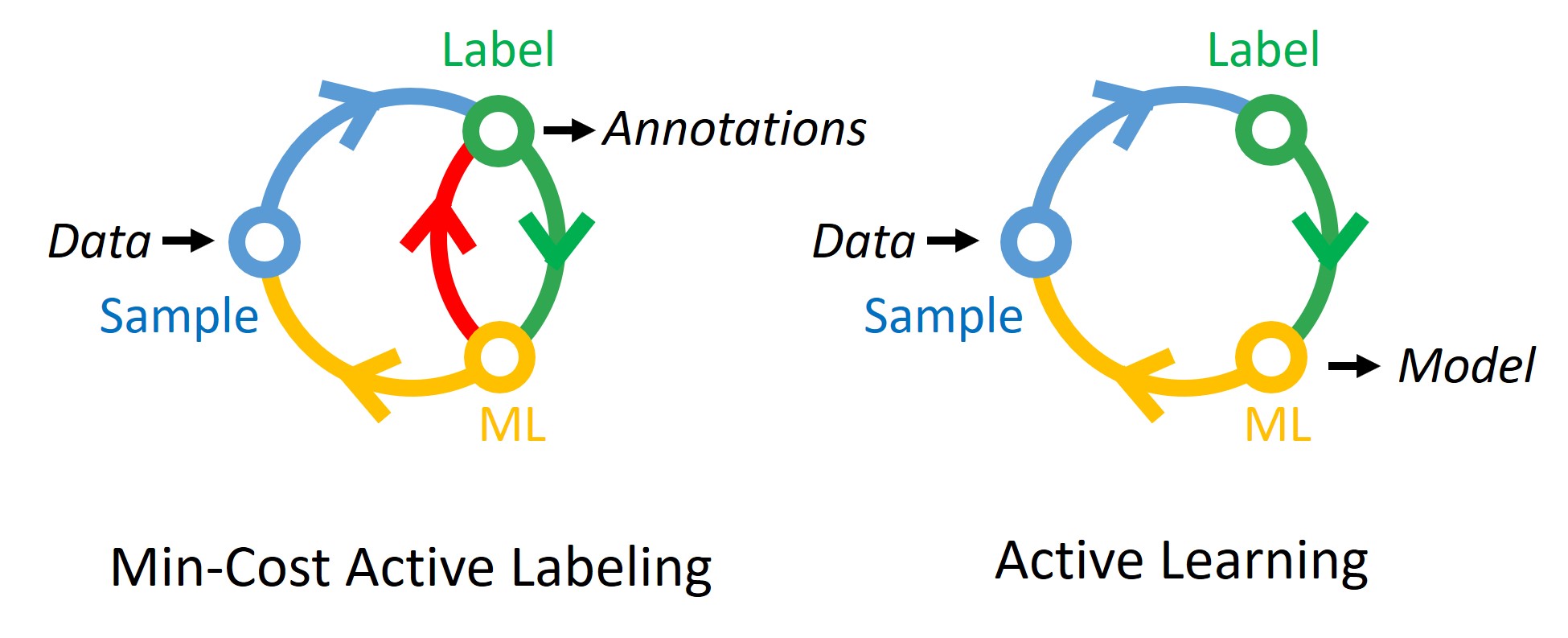
- Data, Auto-labeling, Active Learning. “Data is the new code.” Advanced intelligence is data hungry. Collaborative intelligence is no exception. Therefore it is critical to deal with cost reduction in the development and maintenance of edge ML systems. In collaboration with Microsoft Research, we first built Satyam, a scalable annotation platform on top of azure functions, which was partially integrated into Azure Labeling Service. Our follow-up work MCAL brings machine labeling in the loop, further reducing data labeling cost for machine vision.



